When it comes to industrial applications, selecting the right type of valve is crucial for efficient fluid control. Gate valves and ball valves are two of the most commonly used valves in various industries. Understanding the differences between these two types of valves can help engineers, technicians, and decision-makers choose the most appropriate option for their specific needs.
Both gate and ball valves serve the primary purpose of controlling the flow of fluids, but they differ significantly in design, functionality, and application. This article aims to provide a detailed comparison between gate valves and ball valves, helping you make an informed decision.
Whether you're working in the oil and gas industry, water treatment, or any other sector that requires fluid control, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to select the right valve for your system. Let's dive into the specifics of gate valves versus ball valves.
Read also:Dont Joke Lad A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding The Phrase And Its Impact
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Gate and Ball Valves
- What Are Gate Valves?
- What Are Ball Valves?
- Key Differences Between Gate and Ball Valves
- Applications of Gate Valves
- Applications of Ball Valves
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Gate Valves
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Ball Valves
- Maintenance Tips for Gate and Ball Valves
- Cost Considerations
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Introduction to Gate and Ball Valves
Definition and Importance
Gate valves and ball valves are essential components in fluid control systems. A gate valve uses a gate-like mechanism to control the flow of fluids, while a ball valve relies on a spherical disc with a hole through the center to regulate flow. Both types of valves have unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
What Are Gate Valves?
Gate valves are designed to provide a straight-line flow of fluid and are typically used for isolation purposes. They are not ideal for throttling applications due to their design. Gate valves operate by raising or lowering a gate to allow or stop the flow of fluid.
Design and Operation
Gate valves consist of a body, bonnet, stem, disc (gate), and seat. The gate moves perpendicular to the flow of fluid, which allows for minimal resistance when fully open. Gate valves are available in various materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and bronze, making them suitable for different environments.
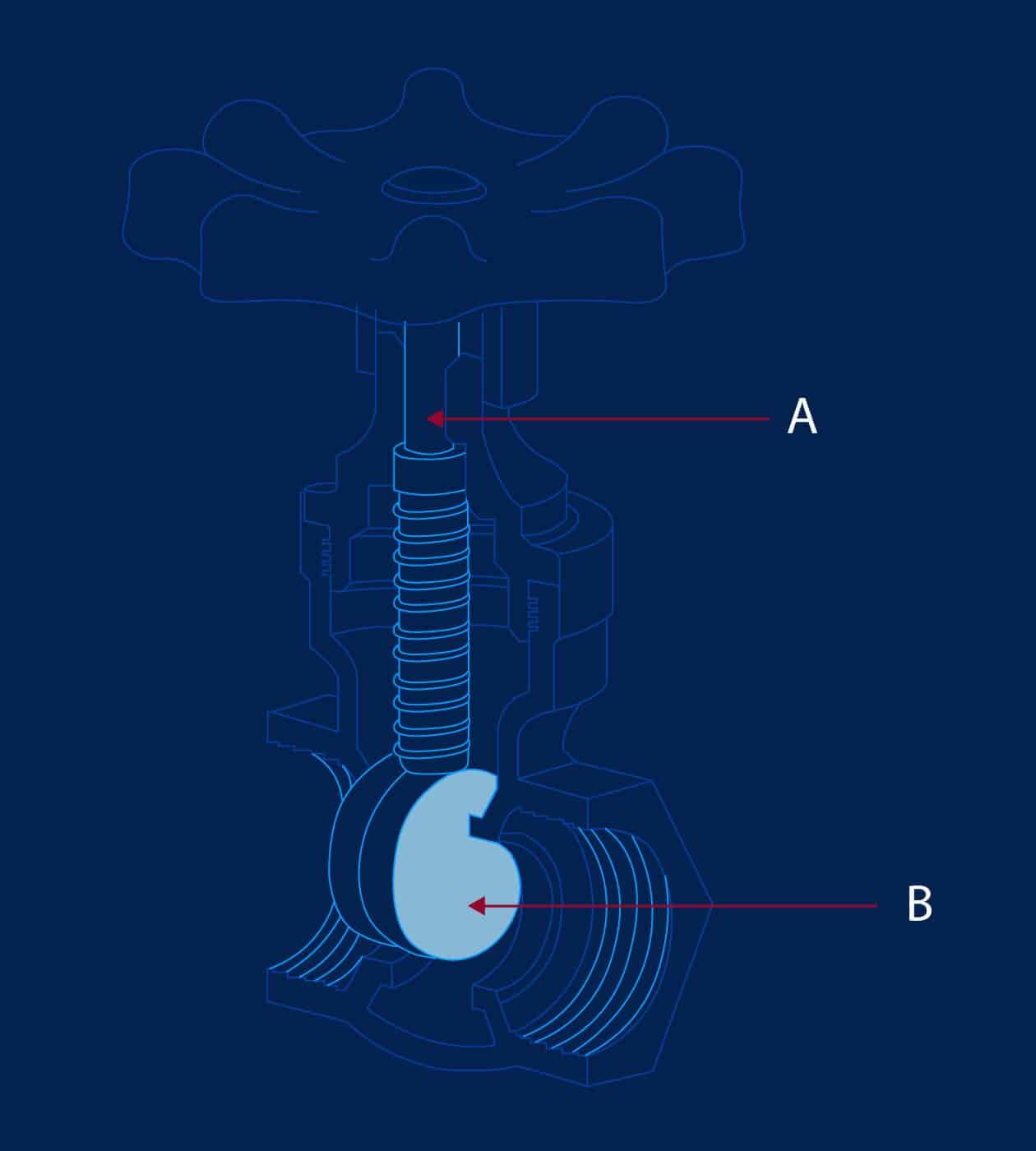
What Are Ball Valves?
Ball valves, on the other hand, use a rotating ball with a hole through the center to control the flow of fluid. When the hole is aligned with the flow direction, the valve is open; when the ball is rotated 90 degrees, the valve is closed.
Design and Operation
Ball valves are known for their quick-shut-off capability and are often used in applications requiring rapid flow interruption. They are available in different types, such as full-port, reduced-port, and V-port ball valves, each serving specific purposes. Ball valves are also available in a variety of materials, including PVC, stainless steel, and brass.
Read also:Is Lena Paul Pregnant Unveiling The Truth Behind The Rumors
Key Differences Between Gate and Ball Valves
The primary differences between gate and ball valves lie in their design, functionality, and application. Below are some key distinctions:
- Design: Gate valves have a linear motion, while ball valves have a rotary motion.
- Flow Control: Gate valves are better suited for fully open or fully closed positions, whereas ball valves can offer precise control over flow rates.
- Maintenance: Ball valves generally require less maintenance compared to gate valves.
Applications of Gate Valves
Gate valves are widely used in industries where fluid flow needs to be fully stopped or fully allowed. Some common applications include:
- Pipeline systems
- Water distribution networks
- Oil and gas extraction
Applications of Ball Valves
Ball valves are preferred in applications requiring quick and reliable shut-off. They are commonly used in:
- Cryogenic applications
- Chemical processing
- Compressed air systems
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gate Valves
Gate valves offer several advantages, but they also come with some drawbacks. Below is a summary:
Advantages
- Minimal pressure drop when fully open
- Suitable for larger pipe sizes
Disadvantages
- Slower operation compared to ball valves
- Not ideal for throttling
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ball Valves
Ball valves also have their own set of pros and cons:
Advantages
- Quick and reliable shut-off
- Compact design
Disadvantages
- May experience wear over time
- Not suitable for large pipe sizes
Maintenance Tips for Gate and Ball Valves
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and efficiency of both gate and ball valves. Below are some maintenance tips:
- Inspect valves regularly for leaks or corrosion
- Lubricate moving parts as needed
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and servicing
Cost Considerations
When considering cost, it's important to evaluate both the initial purchase price and the long-term maintenance expenses. Gate valves are generally more affordable upfront but may require more frequent maintenance. Ball valves, while often more expensive initially, tend to have lower maintenance costs over time.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, both gate valves and ball valves have their own unique strengths and weaknesses. The choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your application. Gate valves are ideal for applications requiring full flow with minimal pressure drop, while ball valves excel in scenarios demanding quick and reliable shut-off.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with gate and ball valves in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into fluid control systems.
Data Sources: