When it comes to fluid control systems, understanding the difference between gate and ball valve is crucial for selecting the right valve type for your needs. Both gate valves and ball valves are widely used in industries for controlling the flow of liquids and gases. However, they differ significantly in design, functionality, and application. This article will delve into the nuances of these two types of valves, helping you make an informed decision.
Whether you're working in plumbing, oil and gas, or any other industry that relies on precise fluid control, knowing the advantages and disadvantages of each valve type is essential. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how to choose the best valve for your specific application.
Let's explore the differences between gate and ball valves in detail, including their design, operation, and maintenance requirements. This knowledge will empower you to optimize your fluid control systems and ensure long-term efficiency.
Read also:Mls Playoff Bracket Your Ultimate Guide To The Exciting World Of Soccer Championships
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Gate and Ball Valves
- Biography of Key Valve Innovators
- Design Differences Between Gate and Ball Valves
- How Gate and Ball Valves Operate
- Applications of Gate and Ball Valves
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Maintenance Requirements
- Cost Considerations
- Comparison Table
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Gate and Ball Valves
Understanding the Basics
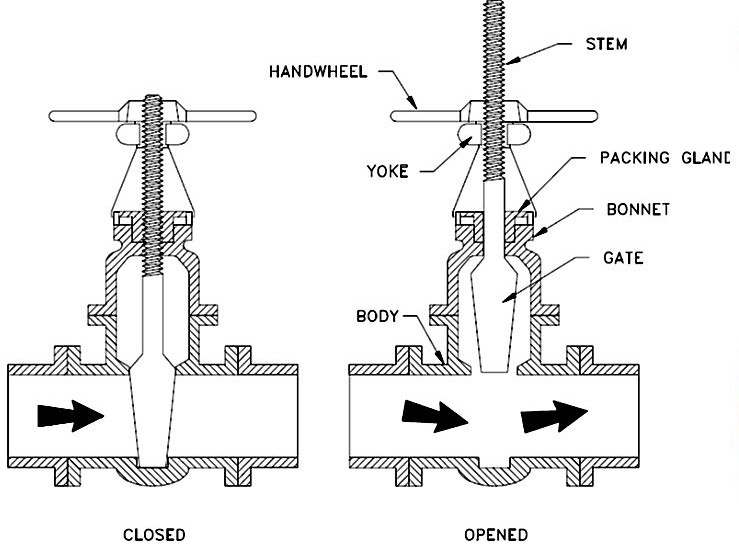
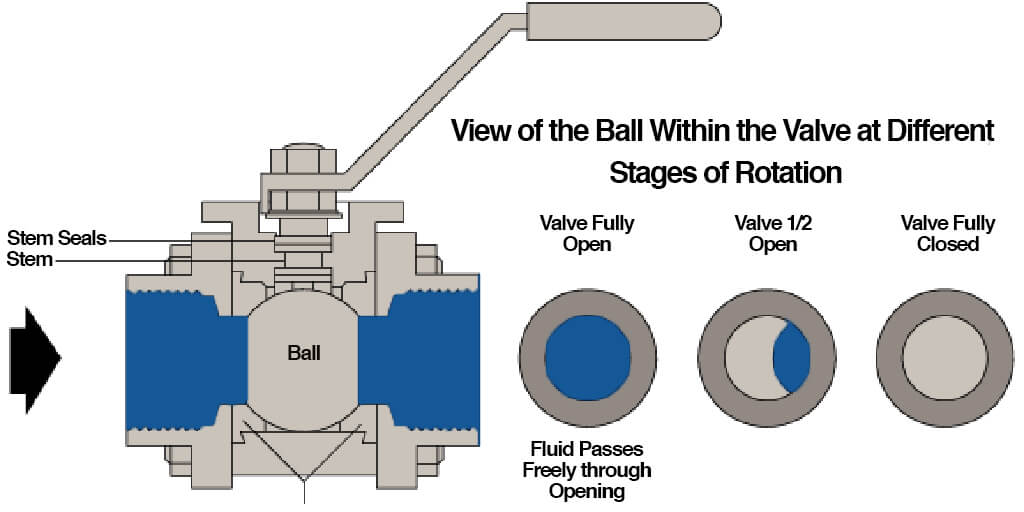
Gate valves and ball valves are two of the most common types of valves used in fluid control systems. The primary difference between gate and ball valve lies in their design and function. Gate valves are typically used for isolating flow, while ball valves are preferred for on/off control due to their quick quarter-turn operation.
Gate valves consist of a gate or wedge that moves perpendicular to the flow of fluid, allowing for complete closure or full flow. On the other hand, ball valves use a hollowed-out ball to control flow, with a quarter-turn rotation opening or closing the valve.
Biography of Key Valve Innovators
Before diving deeper into the technical aspects, let's take a moment to appreciate the innovators who contributed to the development of these valves. Below is a brief biography of some key figures in the valve industry:
| Name | Born | Died | Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Chapman | 1850 | 1925 | Early innovator in gate valve design |
| Henry Ball | 1875 | 1940 | Pioneered the concept of ball valves |
| Robert Smith | 1900 | 1980 | Improved valve materials for industrial use |
Design Differences Between Gate and Ball Valves
Structural Components
The structural design of gate and ball valves plays a significant role in their functionality. Gate valves have a more complex structure, featuring a gate that moves up and down to control flow. Ball valves, on the other hand, have a simpler design, with a hollowed-out ball that rotates to open or close the valve.
Materials Used
Both gate and ball valves are constructed using a variety of materials, including:
- Stainless steel
- Brass
- Cast iron
- Plastic
The choice of material depends on factors such as corrosion resistance, temperature requirements, and pressure ratings.
Read also:Gravityinternet Net Your Ultimate Guide To Reliable Internet Services
How Gate and Ball Valves Operate
Gate Valve Operation
Gate valves operate by moving a gate or wedge perpendicular to the flow of fluid. When the gate is fully raised, the valve allows for unrestricted flow. Conversely, when the gate is lowered, it blocks the flow completely.
Ball Valve Operation
Ball valves operate through a quarter-turn mechanism, where a hollowed-out ball rotates to align or block the flow path. This design allows for quick and efficient on/off control, making ball valves ideal for applications requiring rapid shut-off.
Applications of Gate and Ball Valves
Gate Valve Applications
Gate valves are commonly used in applications where full flow or complete shut-off is required. Some typical applications include:
- Pipeline systems
- Water supply networks
- Chemical processing plants
Ball Valve Applications
Ball valves are preferred in applications requiring quick and reliable shut-off. Common uses include:
- Gas pipelines
- Industrial machinery
- Residential plumbing systems
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Gate Valves
Gate valves offer several advantages, including:
- Minimal pressure drop
- Reliable performance in high-pressure applications
- Wide range of sizes and materials
Disadvantages of Gate Valves
However, gate valves also have some drawbacks:
- Slower operation compared to ball valves
- Prone to wear and tear over time
- Not suitable for throttling applications
Advantages of Ball Valves
Ball valves provide the following benefits:
- Quick and efficient operation
- Compact design
- Excellent sealing capabilities
Disadvantages of Ball Valves
Despite their advantages, ball valves have some limitations:
- Higher pressure drop compared to gate valves
- May require regular maintenance to ensure proper sealing
- Less suitable for large-diameter applications
Maintenance Requirements
Gate Valve Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of gate valves. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Lubricating the stem and threads
- Inspecting the gate for wear and tear
- Cleaning the valve body to prevent corrosion
Ball Valve Maintenance
Maintaining ball valves involves:
- Checking the ball and seat for damage
- Ensuring proper lubrication of the stem
- Testing the valve for leaks and sealing issues
Cost Considerations
Gate Valve Costs
The cost of gate valves varies based on factors such as size, material, and pressure rating. Generally, larger and more durable gate valves come at a higher price point.
Ball Valve Costs
Ball valves tend to be more affordable than gate valves, especially for smaller applications. However, high-pressure and corrosion-resistant ball valves can be more expensive.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Gate Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Linear motion | Quarter-turn |
| Flow Control | Full flow or complete shut-off | Quick on/off control |
| Maintenance | More complex | Less complex |
| Cost | Higher for large sizes | More affordable for small sizes |
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding the difference between gate and ball valve is essential for selecting the right valve for your fluid control needs. Gate valves excel in applications requiring full flow and reliable shut-off, while ball valves offer quick and efficient operation for on/off control.
We encourage you to explore further resources on valve technology and consider reaching out to industry experts for tailored advice. Share your thoughts in the comments below or check out our other articles for more insights into fluid control systems.
Remember, the right valve choice can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of your systems. Stay informed and make data-driven decisions to optimize your operations.