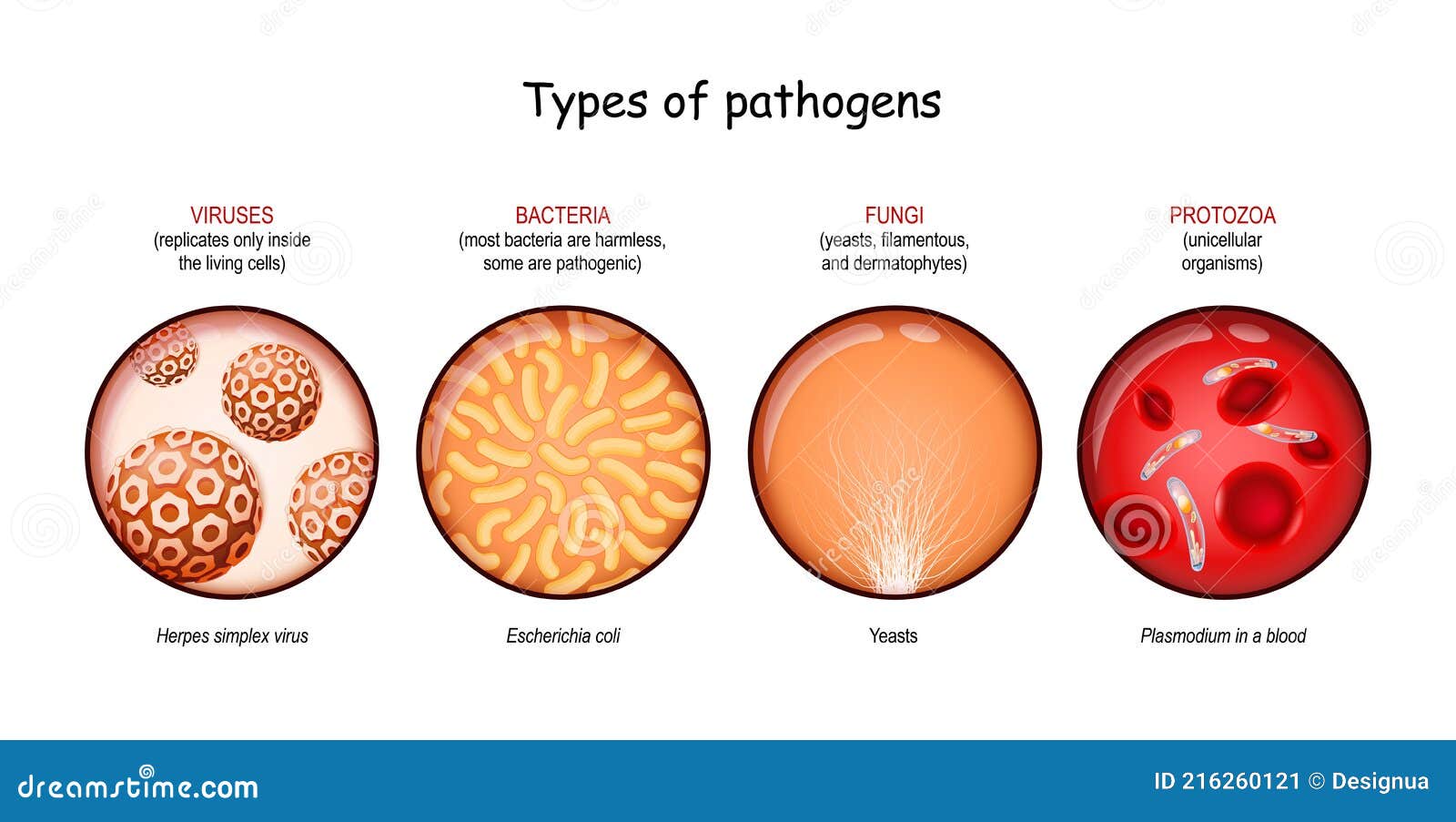
Protozoa organisms are among the most fascinating and essential microorganisms on the planet. These single-celled creatures play a critical role in ecosystems, influencing nutrient cycles, food webs, and even human health. Understanding protozoa is vital not only for scientific research but also for addressing global challenges such as disease control and environmental sustainability.
Protozoa are often overlooked due to their microscopic size, but their impact on the world is anything but small. These organisms exhibit incredible diversity in terms of structure, function, and ecological roles. From aiding in decomposition to causing diseases like malaria, protozoa are both allies and adversaries in the natural world.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of protozoa organisms, exploring their characteristics, classification, ecological importance, and their relationship with humans. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the microbial world, this article will provide you with a deep understanding of protozoa and their significance.
Read also:Houghton Mariah The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Protozoa
- Classification of Protozoa
- Ecological Importance of Protozoa
- Protozoa in Human Health
- Reproduction and Life Cycles
- Protozoa and the Environment
- Research and Studies on Protozoa
- Future Perspectives
- Conclusion
Introduction to Protozoa
Protozoa organisms are single-celled eukaryotes that belong to the kingdom Protista. Despite their small size, they possess complex structures and functions that allow them to thrive in diverse environments. Protozoa are found in almost every habitat, from freshwater lakes and oceans to soil and even within the human body.
These organisms are characterized by their ability to move independently, which sets them apart from other microorganisms like bacteria. Protozoa use various mechanisms for locomotion, such as pseudopodia, flagella, or cilia, depending on their classification. Their versatility and adaptability make them crucial players in the ecosystem.
Protozoa are classified into several groups based on their morphology, mode of nutrition, and method of movement. Understanding these classifications is essential for comprehending their roles in nature and their interactions with other organisms.
Classification of Protozoa
Protozoa are traditionally divided into four main groups based on their structural and functional characteristics. Each group exhibits unique features that define their behavior and ecological roles. Below is an overview of these classifications:
Amoeba
Amoebas are characterized by their ability to extend pseudopodia, which are temporary projections of their cytoplasm. These structures enable them to move and engulf food particles through a process called phagocytosis. Amoebas are commonly found in freshwater and soil environments, where they play a significant role in nutrient cycling.
- Example: Amoeba proteus
- Ecological Role: Decomposers and predators of bacteria
Flagellates
Flagellates are protozoa that use flagella, whip-like structures, for locomotion. These organisms are highly diverse and can be free-living or parasitic. Some flagellates are pathogenic, causing diseases such as African sleeping sickness and giardiasis in humans.
Read also:David Bromstad Age Unveiling The Life And Career Of A Renowned Artist
- Example: Trypanosoma brucei
- Pathogenic Role: Causes African sleeping sickness
Ecological Importance of Protozoa
Protozoa organisms play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. They are essential components of aquatic and terrestrial food webs, acting as both predators and prey. By consuming bacteria, algae, and other microorganisms, protozoa help regulate microbial populations and recycle nutrients.
In addition to their role in nutrient cycling, protozoa also contribute to the decomposition of organic matter. This process releases essential nutrients back into the environment, supporting plant growth and overall ecosystem health. Furthermore, protozoa serve as a food source for larger organisms, such as zooplankton and small fish.
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of protozoa in climate regulation. By influencing carbon and nitrogen cycles, these organisms help mitigate the effects of global warming and maintain ecological stability.
Protozoa in Human Health
While many protozoa are beneficial, some species are responsible for serious diseases in humans. These parasitic protozoa invade the human body, causing infections that can lead to severe health complications. Understanding the biology and life cycles of these organisms is crucial for developing effective treatments and prevention strategies.
Malaria
Malaria is one of the most well-known diseases caused by protozoa. It is transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes, which carry the parasite Plasmodium. Malaria affects millions of people worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Pathogen: Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, fatigue
- Treatment: Antimalarial drugs such as artemisinin-based combination therapies
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is another common protozoal infection that affects the digestive system. It is caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia, which is transmitted through contaminated water or food. This disease primarily affects the intestines, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and dehydration.
- Pathogen: Giardia lamblia
- Symptoms: Diarrhea, bloating, nausea, weight loss
- Treatment: Antibiotics such as metronidazole or tinidazole
Reproduction and Life Cycles
Protozoa reproduce through various methods, including binary fission, budding, and sexual reproduction. These processes allow them to adapt to changing environmental conditions and ensure the survival of their species. Understanding the life cycles of protozoa is essential for controlling their populations, especially in the case of parasitic species.
For example, the life cycle of Plasmodium involves multiple stages, including sporozoites, merozoites, and gametocytes. Each stage occurs in a specific host, such as the mosquito or human liver and blood cells. By targeting specific stages of the life cycle, scientists can develop more effective treatments and vaccines.
Protozoa and the Environment
Protozoa organisms are highly sensitive to environmental changes, making them excellent indicators of ecosystem health. Changes in water quality, temperature, and pollution levels can significantly impact protozoan populations, which in turn affect the entire food web. Monitoring protozoa can provide valuable insights into the health of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Furthermore, protozoa play a critical role in bioremediation, the process of using microorganisms to clean up environmental pollutants. Certain protozoa species can break down harmful substances such as heavy metals and hydrocarbons, helping to restore damaged ecosystems.
Research and Studies on Protozoa
Ongoing research on protozoa is expanding our understanding of these fascinating organisms. Advances in molecular biology, genetics, and microscopy have enabled scientists to study protozoa in unprecedented detail. This research has led to new discoveries about their biology, ecology, and potential applications in medicine and environmental science.
For instance, studies on the genome of Plasmodium have identified potential drug targets for malaria treatment. Similarly, research on the role of protozoa in nutrient cycling has highlighted their importance in sustainable agriculture and climate change mitigation.
Future Perspectives
The future of protozoa research holds great promise for addressing global challenges. By harnessing the capabilities of these organisms, scientists can develop innovative solutions for healthcare, environmental conservation, and food security. Continued investment in research and technology will be essential for unlocking the full potential of protozoa.
Collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders will also be crucial for translating scientific discoveries into practical applications. By working together, we can ensure a sustainable future for both humans and the environment.
Conclusion
Protozoa organisms are remarkable microorganisms that play vital roles in ecosystems and human health. From regulating microbial populations to causing diseases like malaria, protozoa have a profound impact on the world. Understanding these organisms is essential for addressing global challenges and ensuring a sustainable future.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about protozoa in the comments section below. Feel free to explore our other articles on microbiology and related topics for more in-depth information. Together, let's continue to expand our knowledge and appreciation of the microbial world!